CRISPRCas9 technology against noncoding regions, consideration of these regions is of immense importance while orchestrating the models GC content in PAM proximal seed region, intact RAR and 3rd stem loop secondary structures, and free accessibility of nucleotides in seed region and tracrRNA MaliketalBioscription Menu Skip to content CRISPR/Cas9 is a versatile genomeediting technology that is widely used for studying the functionality of genetic elements, creating genetically modified organisms as well as preclinical research of genetic disorders

Diversification Of The Crispr Toolbox Applications Of Crispr Cas Systems Beyond Genome Editing The Crispr Journal
Seed region crispr
Seed region crispr- 7 Box AM, McGuffie MJ, O'Hara BJ and Seed KD 16 Functional analysis of bacteriophage immunity through a type IE CRISPRCas system in Vibrio cholerae and its application in bacteriophage genome engineering Journal of Bacteriology –590 6 Dalia AB, Seed KD, Calderwood SB and Camilli A 15Coli subtype CRISPR/Cas system, the requirements for crRNA match ing are strict only for a sevennucleotide seed region of a protospa cer immediately following the essential protospaceradjacent motif Mutations in the seed region abolish CRISPR/Cas mediated immunity by reducing the binding affinity of the crRNAguided Cascade complex to




Origins And Evolution Of Crispr Cas Systems Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society B Biological Sciences
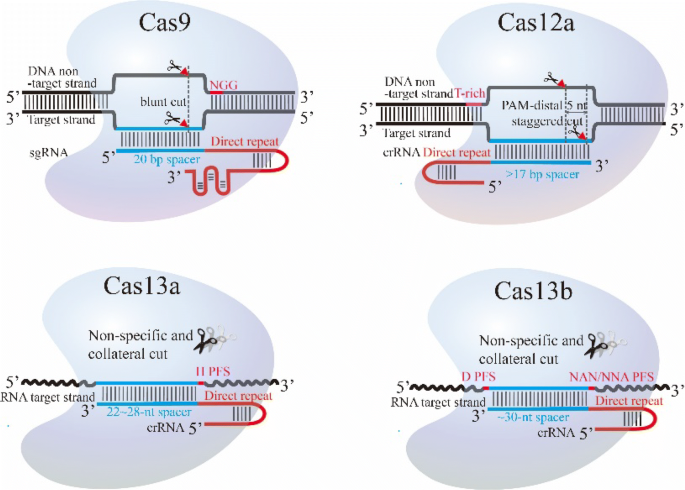
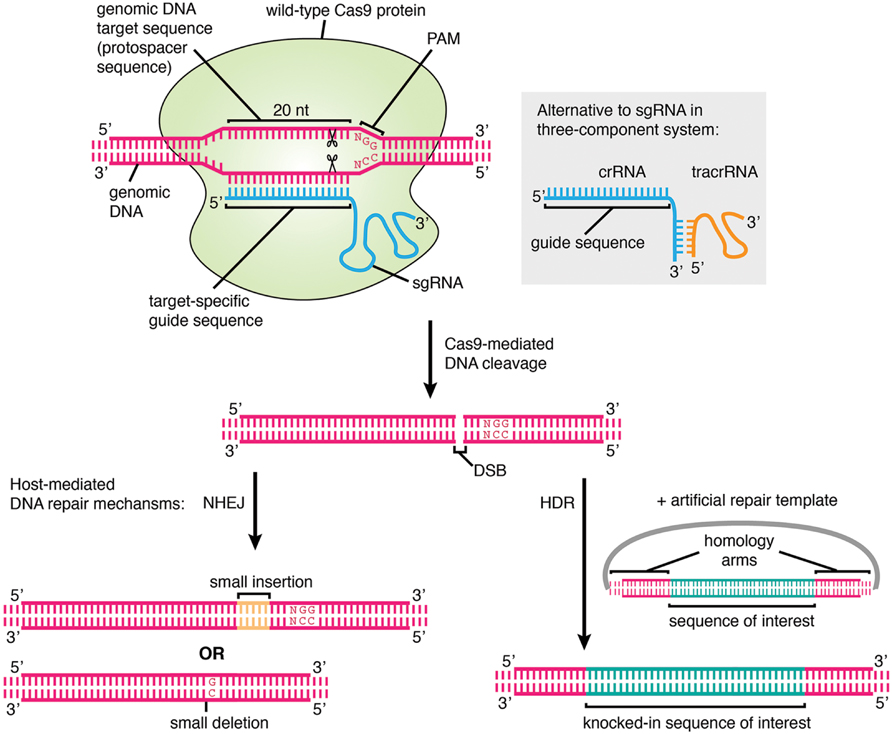
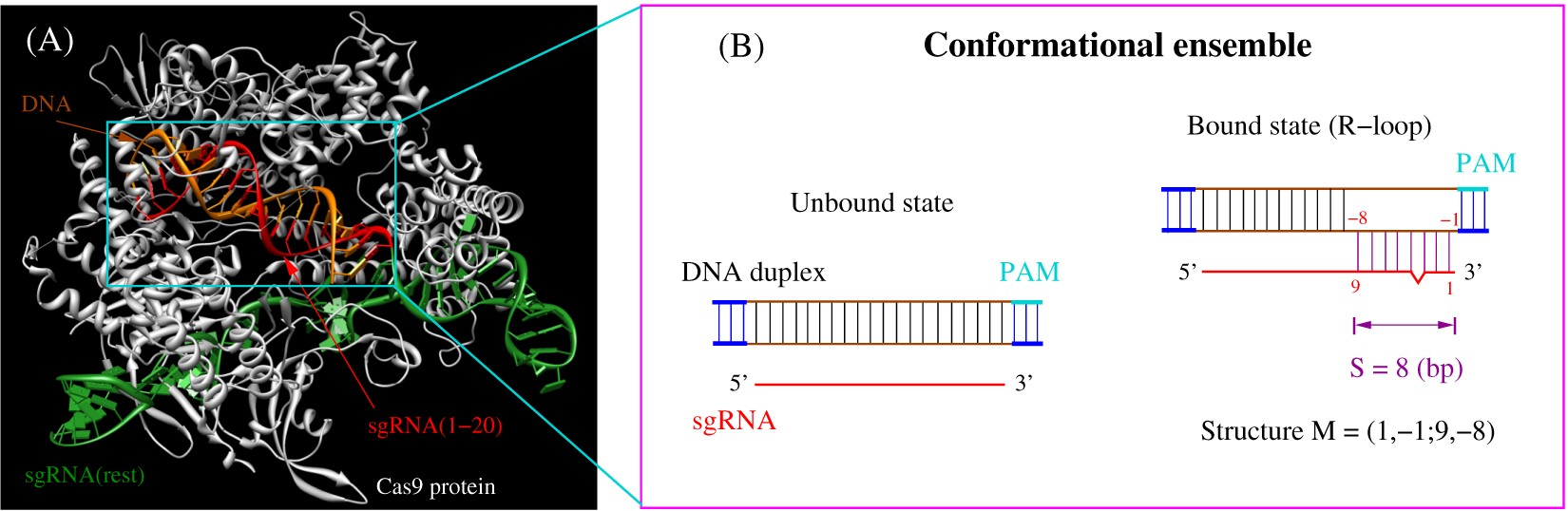
CRISPR was originally employed to knock out target genes in various cell types and organisms, but modifications to various Cas enzymes have extended CRISPR to selectively activate/repress target genes, purify specific regions of DNA, image DNA in live cells, and precisely edit DNA and RNACas9 is a DNA endonuclease with two active domains (red triangles) cleaving each of the two DNA strands three nucleotides upstream of the PAM The five nucleotides upstream of the PAM are defined as the seed region for target recognition Applications of CRISPRCas9 Experiments suggest that the nt long protospacer can be divided into two regions, the seed (PAMproximal) region within 10 base pairs from the PAM and the nonseed (PAMdistal) region with 10
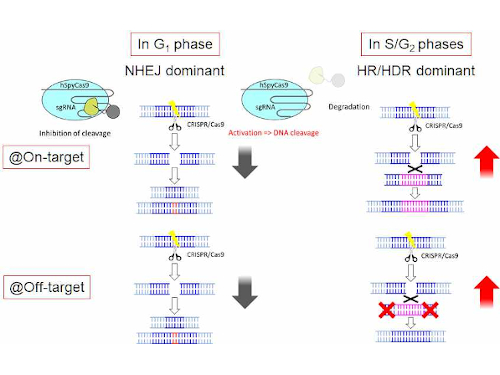
In addition, despite the high specificity of the CRISPRCas9 system, offtarget mutations can occur at sites that have sequence similarity to the target site 24,25,26, especially when there are no mismatches in the PAMproximal 8–12 nucleotide 'seed region' of the guide sequence 27,28,29,30 Such offtarget sites may be present in non Mutations in the seed region abolish CRISPR/Cas mediated immunity by reducing the binding affinity of the crRNAguided Cascade complex to protospacer DNA We propose that the crRNA seed sequence plays a role in the initial scanning of invader DNA for a match, before base pairing of the fulllength spacer occurs, which may enhance theCRISPRRT (CRISPR R NA T argeting) is a web application to help biologists design optimal crRNAs for the CRISPRC2c2/Cas13a system CRISPRRT is essentially composed of many interfaces and a backend pipeline Interfaces are implemented by PHP and JavaScript code, which are used to accept user inputs and interactively display the results
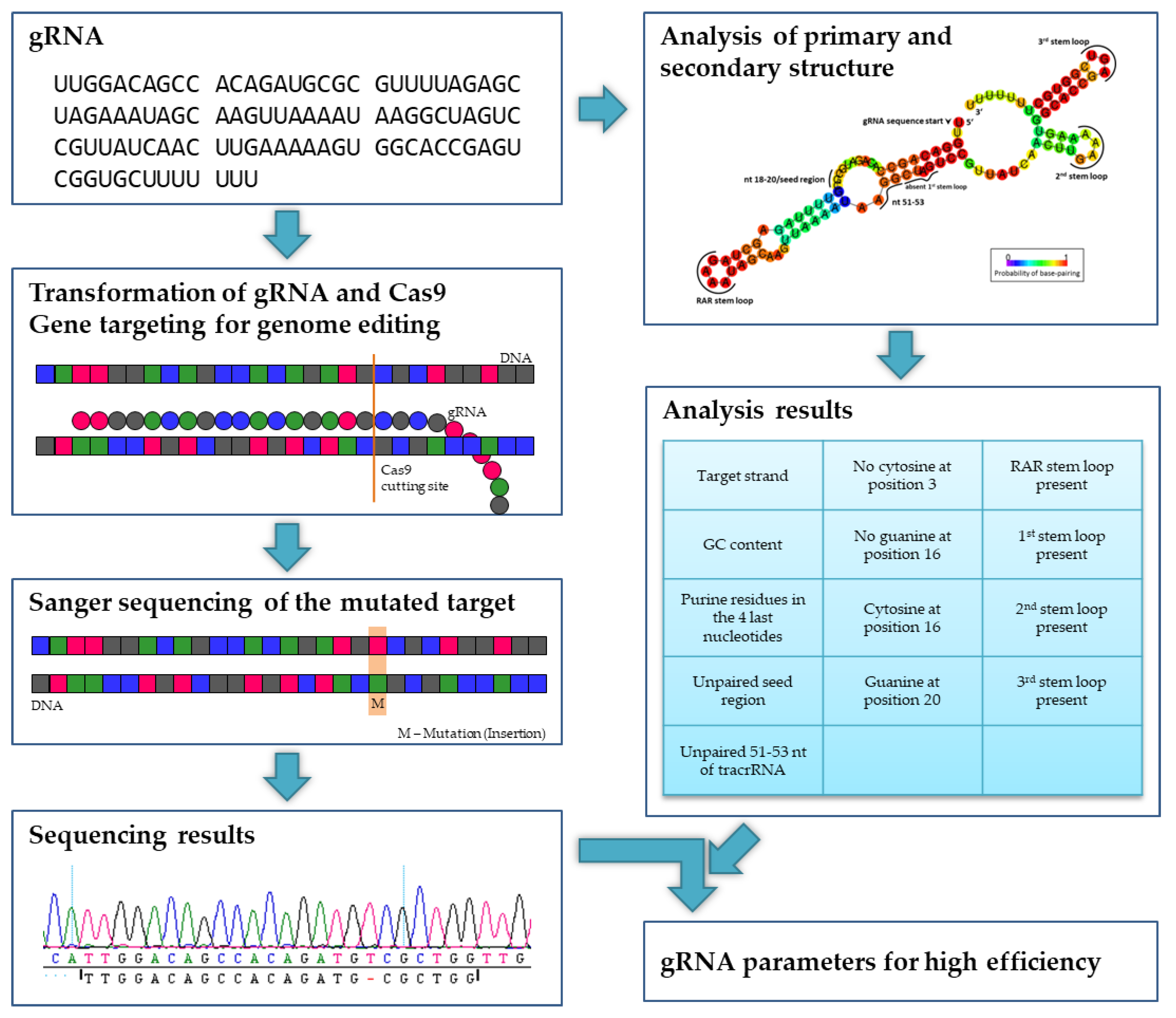
The number is the number of potential cut sites adjacent to an NGG or NAG sequence that can be annealed to by the 12mer seed region of the CRISPR (not the entire mer) with fewer than two mismatches While this number is not the exact number of offtargets expected, lower numbers are better The 3′ end of the guide sequence, also known as the "seed region", plays a critical role in recognition of target sequence Thus, based on structural analysis, accessibility of the last three bases in the seed region was a prominent feature to differentiate functional sgRNAs from nonfunctional ones (Fig 1b) The CRISPRCas9 system has recently evolved as a powerful mutagenic tool for targeted genome editing The impeccable functioning of the system depends on the optimal design of single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) that mainly involves sgRNA specificity and ontarget cleavage efficacy Several research groups have designed algorithms and models, trained on mammalian



Seedquest Central Information Website For The Global Seed Industry




Off Target Genome Editing Wikipedia
The kinetic basis of CRISPRCas offtargeting rules Authors Misha Klein1, Behrouz EslamiMossallam1, Dylan Gonzalez Arroyo1,2, Martin Depken1 Author affiliations between mismatches outside the seed region that allows for the cleavage of targets with multiple mismatches This suggests that the presence of an intact PAM accompanied by perfect base pairing of the sevennucleotide crRNA seed sequence (comprising positions 1–5, 7, and 8) with the seed region of target DNA is actively monitored by the Cascade complex and is a prerequisite for the initiation of CRISPR interference Using thousands of guide RNAs with 1, 2 or 3 singleletter mismatches to their target RNA, they identified a critical "seed" region that is exquisitely sensitive to



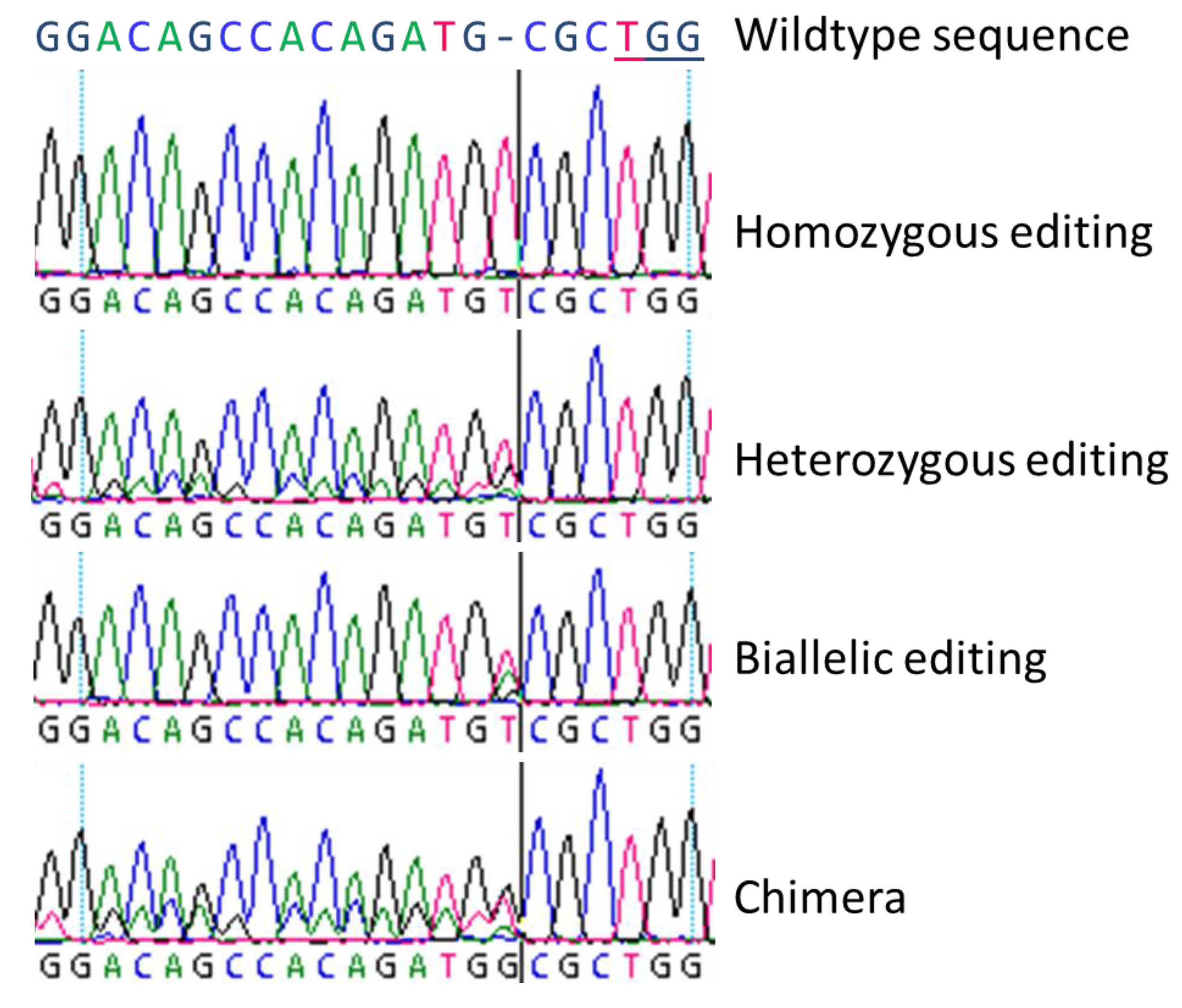
High Fidelity Crispr Cas9 Increases Precise Monoallelic And Biallelic Editing Events In Primordial Germ Cells Engormix




Crispr Cas12a More Precise Than Crispr Cas9
The spacer segment, which is complementary to the target DNA, contains a seed region with eight nucleotides length Seed region flanks at the initial part of the spacer and plays a notable role in the target specificity of CRISPR–Cpf1 system (Fig 3) The clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)/CRISPR associated protein (Cas) system, an adaptive immune system found in many archaea and bacteria, has recently emerged as Using thousands of guide RNAs with 1, 2 or 3 singleletter mismatches to their target RNA, they identified a critical "seed" region that is exquisitely sensitive to mismatches between the CRISPR guide and the target This discovery will aid scientists in designing guide RNAs to avoid offtarget activity on unintended target RNAs



Www Nobelprize Org Uploads 10 Advanced Chemistryprize Pdf




The Crispr Cas9 System For Crop Improvement Progress And Prospects Intechopen
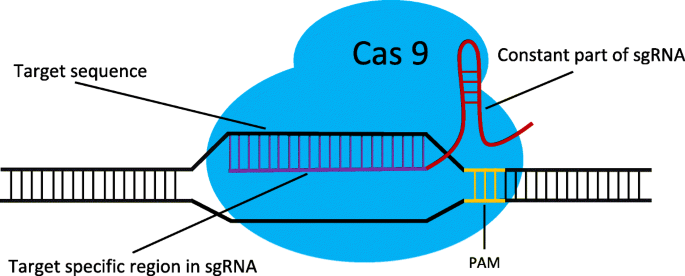
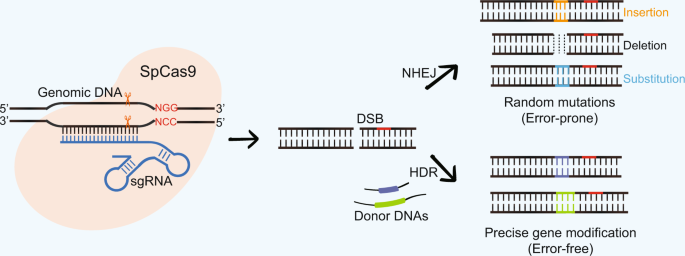
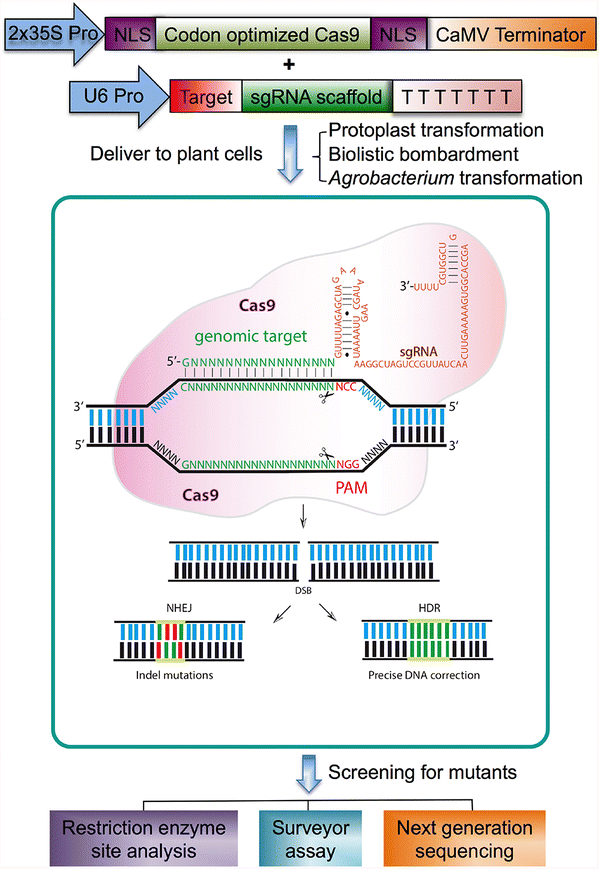
CRISPRCas9 is a simple twocomponent system that allows researchers to precisely edit any sequence in the genome of an organism This is achieved by guide RNA, which recognizes the target sequence, and the CRISPRassociated endonuclease (Cas) that cuts the targeted sequence Researchers across the globe who are adopting this technology are bound to come across anCas13a, a type VIA CRISPRCas RNAguided RNA ribonuclease, degrades invasive RNAs targeted by CRISPR RNA (crRNA) and has potential applications in RNA technology To understand how Cas13a is activated to cleave RNA, we have determined the crystal structure of Leptotrichia buccalis (Lbu) Cas13a boun 5154, 56 The central seed region of type VIA systems is in stark contrast with other RNAguided nucleases (eg, type II and type V CRISPRCas effectors) that utilize solventaccessible preordered proteinbound seed regions, which is energetically favorable for target search, mismatch discrimination, and targetguide duplex formation




Addgene Crispr Guide



Www Cell Com Molecular Plant Pdf S1674 52 16 4 Pdf
CRISPRCas9, SpCas9, the seed region includes 10 PAMproximal bases (position 1–10,Figure 1B) The nucleotides in the seed region are recognized by Cas9 protein via the arginine residues in the bridge helix and the REC1 domains within the REC lobe This seed region serves as a sensitive Thus, the CRISPR target was designed in the seed sequence of mature miRNA Tilapia miRNA125 was selected as the target to examine whether mutation could be induced in the seed region using CRISPR/Cas9 gRNA containing restriction enzyme Mse I was designed in the seed sequence of miRNA125 Coinjection of gRNA and Cas9 mRNA led to indels CRISPRCas12a DNA cleavage patterns, as evaluated in a quantitative kinetics study, suggest that the less frequently used Cas12a enzyme has greater target specificity than the more popular Cas9




Gene Editing With Crispr Cas9 Rna Directed Nuclease Circulation Research




Cas9 Cuts And Consequences Detecting Predicting And Mitigating Crispr Cas9 On And Off Target Damage Newman Bioessays Wiley Online Library
The clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)/CRISPRassociated nuclease 9 (Cas9) system is a genome editing technology transforming the field of plant biology by virtue of the system's efficiency and specificityMany bacterial clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)–CRISPRassociated (Cas) systems employ the dual RNA–guided DNA endonuclease Cas9 to defend against invading phages and conjugative plasmids by introducing sitespecific doublestranded breaks in This RNA "seed region" is thus poised to initiate recognition of the DNA target sequence Science , this issue p Bacterial adaptive immunity uses CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)–associated (Cas) proteins together with CRISPR transcripts for foreign DNA degradation




Diversification Of The Crispr Toolbox Applications Of Crispr Cas Systems Beyond Genome Editing The Crispr Journal




Dr Gaetan Burgio Md Phd A Twitter This Is A Very Well Performed Study Demonstrating On A Massively Parallel Crispri Assay For Crispr Fncas12a 1 Tttttv Pam Sequence Should Be Preferred For
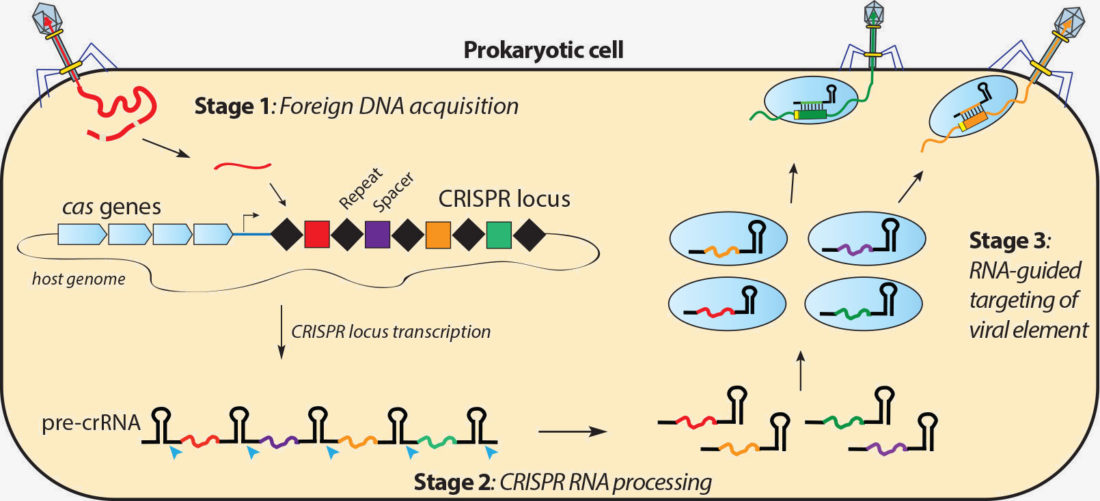
Guide RNA (gRNA) is a piece of RNAs that function as guides for RNA or DNAtargeting enzymes, which they form complexes with Very often these enzymes will delete, insert or otherwise alter the targeted RNA or DNA They occur naturally, serving important functions, but can also be designed to be used for targeted editing, such as with CRISPRCas9Home Journal of BacteriologySpacers/protospacers In a bacterial genome, CRISPR loci contain "spacers" (viral DNA inserted into a CRISPR locus) that in type II adaptive immune systems were created from invading viral or plasmid DNA (called "protospacers") Upon subsequent invasion, a CRISPRassociated nuclease such as Cas9 attaches to a tracrRNA–crRNA complex, which guides Cas9 to the invading




Multiple Stepwise Gene Knockout Using Crispr Cas9 In




Synthetic Crispr Rna Cas9 Guided Genome Editing In Human Cells Pnas
CRISPR/Cas9 has become one of the most promising techniques for genome editing in plants and works very well in poplars with an Agrobacteriummediated transformation systemWe selected twelve genes, including SOC1, FUL, and their paralogous genes, four NFPlike genes and TOZ19 for three different research topics The gRNAs were designed for editing, and, together Using thousands of guide RNAs with 1, 2 or 3 singleletter mismatches to their target RNA, they identified a critical "seed" region that is exquisitely sensitive to mismatches between the CRISPRThe clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)associated enzyme Cas9 is an RNAguided nuclease that has been widely adapted for genome editing in eukaryotic cells However, the in vivo target specificity of Cas9 is poorly understood and most studies rely on in




Figure 2 From Hybridization Kinetics Explains Crispr Cas Off Targeting Rules Semantic Scholar




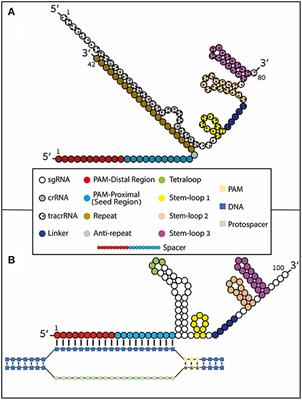
Sequence Recognition And Structure Of Synthetic Crispr Rna A Download Scientific Diagram
Region, including the Drosha processing site and seed region using the CRISPR/Cas system as a novel tool We choose miR93, a critical oncomiRNA from a cluster, as the target By establishing multiple cell lines carrying various mutants and exploring the consequences of genomic alteration, we showed that smallThe seed region, which, for CRISPR Cas enzymes, is a subset of nucleotides within the crRNA that base pairs with PAMproximal nucleotides, is highly sensitive against mismatches and is, therefore, critical for target affinity Characteristic properties of type III CRISPRCas systems include recognition of target RNA (rather than DNA) and the subsequent induction of a multifaceted immune response This involves sequencespecific cleavage of a target RNA and production of cyclic oligoadenylate (cOA) second messenger molecules that may trigger dormancy or cell death In this study, we




Crispr Diagnosis And Therapeutics With Single Base Pair Precision Trends In Molecular Medicine




Using An Endogenous Crispr Cas System For Genome Editing In The Human Pathogen Clostridium Difficile Applied And Environmental Microbiology
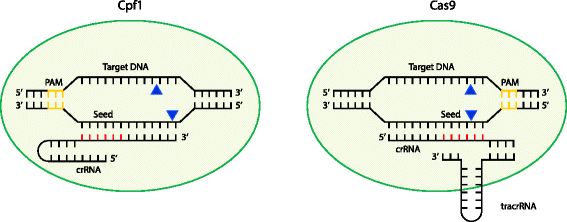
We next evaluated the sequence specificity of CRISPRCasmediated removal We introduced different point mutations into the seed region of the αftsA spacer , where the seed region for the type IE CRISPRCas system in E coli was previously identified as the first through fifth, seventh, and eighth nucleotides flanking the PAM (9, 12)Step 2 Choose your reference genome Reference genome Choose an organism Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 ASM9858v3 NCBI Ensembl Thale cress (Arabidopsis thaliana) genome TAIR1027 Ensembl Rice (Oryza sativa) genome IRGSP1027 Ensembl Human (Homo sapiens) genome GRCh31 Ensembl Mouse (Mus musculus) genome GRCm31 Note that the guide RNA in Cas9 is an RNA duplex involving crRNA and transactivating CRISPR RNA (tracrRNA), whereas Cpf1 uses a single crRNA Upon sufficient complementarity in the seed region (red), Cpf1 and Cas9 nucleases will make two singlestranded cuts (blue triangles) resulting in a doublestranded break




Genome Modification By Crispr Cas9 Ma 14 The Febs Journal Wiley Online Library




Crispr Cas9 Methodology For The Generation Of Knockout Deletions In Caenorhabditis Elegans G3 Genes Genomes Genetics
Mutations in the seed region abolish CRISPR/Cas mediated immunity by reducing the binding affinity of the crRNAguided Cascade complex to protospacer DNA Highlights • Physical model shows CRISPR/Argonaute offtargeting rules to be kinetic in origin • Seed region and mismatchpattern dependence is due to the kinetics of hybridization • Binding is more promiscuous than cleavage due to kinetically stalled hybridization •Mutations in the seed region abolish CRISPR/Cas mediated immunity by reducing the binding affinity of the crRNAguided Cascade complex to protospacer DNA



Arxiv Org Pdf 1712




Crispr Cas Systems In Genome Editing Methodologies And Tools For Sgrna Design Off Target Evaluation And Strategies To Mitigate Off Target Effects Manghwar Advanced Science Wiley Online Library



Class 2 Crispr Cas An Expanding Biotechnology Toolbox For And Beyond Genome Editing Cell Bioscience Full Text




Origins And Evolution Of Crispr Cas Systems Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society B Biological Sciences




Dynamics Of Staphylococcus Aureus Cas9 In Dna Target Association And Dissociation Embo Reports



Plos One Efficient Crispr Cas9 Mediated Gene Editing In Arabidopsis Thaliana And Inheritance Of Modified Genes In The T2 And T3 Generations



Www Diva Portal Org Smash Get Diva2 Fulltext01 Pdf




Impact Of Different Target Sequences On Type Iii Crispr Cas Immunity Journal Of Bacteriology



Full Article Defining The Seed Sequence Of The Cas12b Crispr Cas Effector Complex
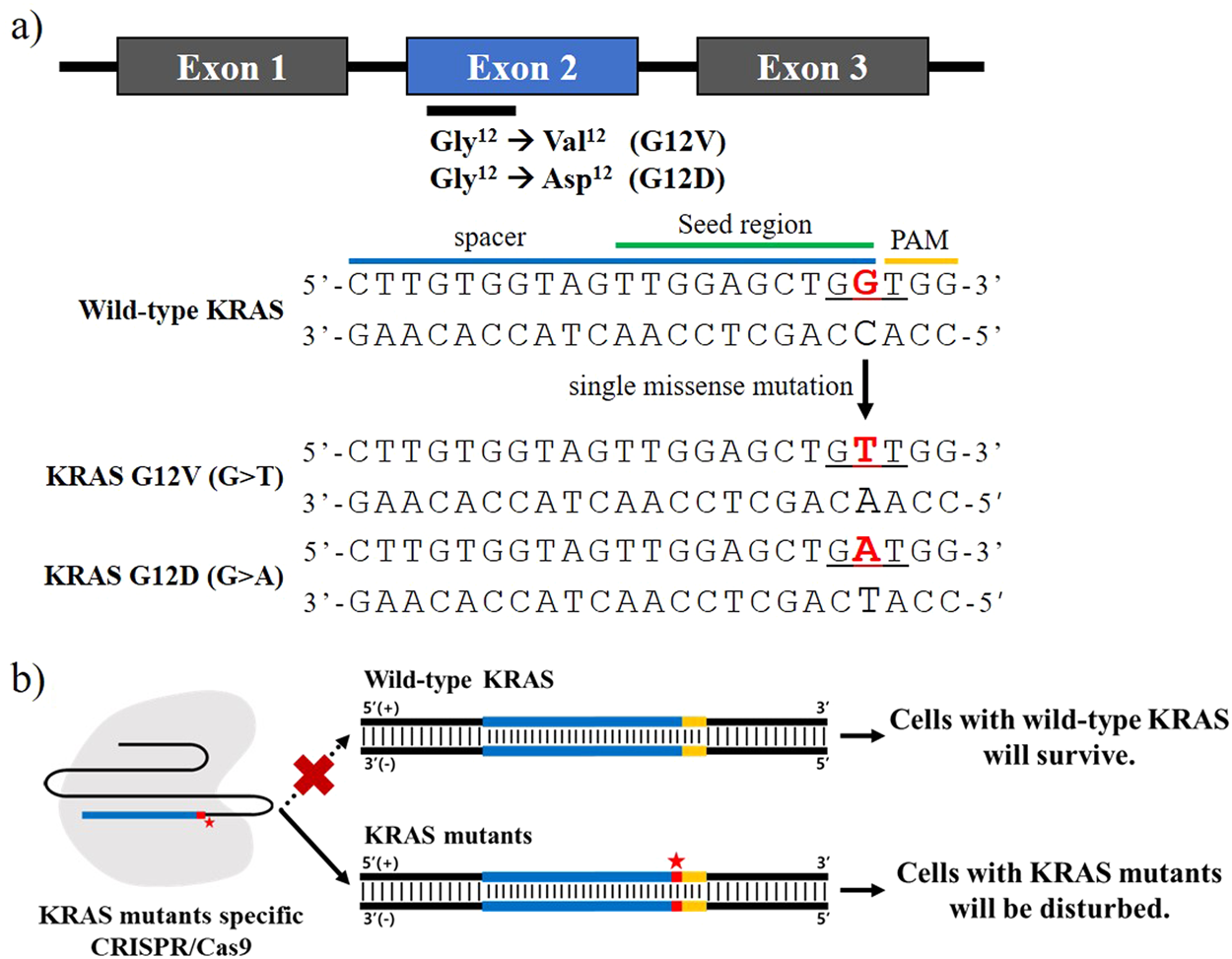



Selective Targeting Of Kras Oncogenic Alleles By Crispr Cas9 Inhibits Proliferation Of Cancer Cells Scientific Reports



Frontiers A New Age In Functional Genomics Using Crispr Cas9 In Arrayed Library Screening Genetics




Crispr Cas9 Abm Inc



Offscan A Universal And Fast Crispr Off Target Sites Detection Tool Bmc Genomics Full Text




Addgene Crispr Guide




Addgene Crispr Guide




Computational Approaches For Effective Crispr Guide Rna Design And Evaluation Sciencedirect




The Magic Cut On Target Dna By Crispr Cas9 Bioscope



Frontiers Using Synthetically Engineered Guide Rnas To Enhance Crispr Genome Editing Systems In Mammalian Cells Genome Editing



Academic Oup Com G3journal Article Pdf 9 1 287 G3journal0287 Pdf




One Or Two Mismatches In The Seed Can Be Tolerated For Crispr Activity Download Scientific Diagram



Crispr Technology Is Revolutionizing The Improvement Of Tomato And Other Fruit Crops Horticulture Research




Very Fast Crispr Using Caged Deoxythymidine




Off Target Effects In Crispr Cas9 Mediated Genome Engineering Sciencedirect




Rnai Shortcomings Is It Time For You To Switch To Crispr



1




Interference By Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat Crispr Rna Is Governed By A Seed Sequence Pnas



Dr Gaetan Burgio Md Phd Auf Twitter Interesting This Paper Published Today In Naturemicrobiol Shows That Crispr Cas9 Or Cas12a Cpf1 Can Display An Inherent Potent Nicking Activity In Yeast This Nicking



Crispr Systems Doudna Lab




Enhancement Of Target Specificity Of Crispr Cas12a By Using A Chimeric Dna Rna Guide Biorxiv




Generating Crispr Cas9 Mediated Monoallelic Deletions To Study Enhancer Function In Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells Protocol



Applications And Roles Of The Crispr System In Genome Editing Of Plants Springerlink



The Cpf1 Crispr Cas Protein Expands Genome Editing Tools Genome Biology Full Text



Crispr Cas9 Cleavage Efficiency Correlates Strongly With Target Sgrna Folding Stability From Physical Mechanism To Off Target Assessment Scientific Reports



Ijms Free Full Text Evaluating The Efficiency Of Grnas In Crispr Cas9 Mediated Genome Editing In Poplars Html




The Crispr Cas9 System For Plant Genome Editing And Beyond Sciencedirect



Www Nobelprize Org Uploads 10 Advanced Chemistryprize Pdf



1



Document For Crispr Ge




Crispr Cas9 Gene Drives In Genetically Variable And Nonrandomly Mating Wild Populations Science Advances




The Magic Cut On Target Dna By Crispr Cas9 Bioscope



Ijms Free Full Text Evaluating The Efficiency Of Grnas In Crispr Cas9 Mediated Genome Editing In Poplars Html




Rna Guided Genome Editing In Plants Using A Crispr Cas System Molecular Plant



Www Asktheeu Org En Request 7766 Response Attach 23 06 at 17 rnai based techniques accelerated breeding and crispr cas Pdf Cookie Passthrough 1




Crispr Cas9 Gene Editing Applications
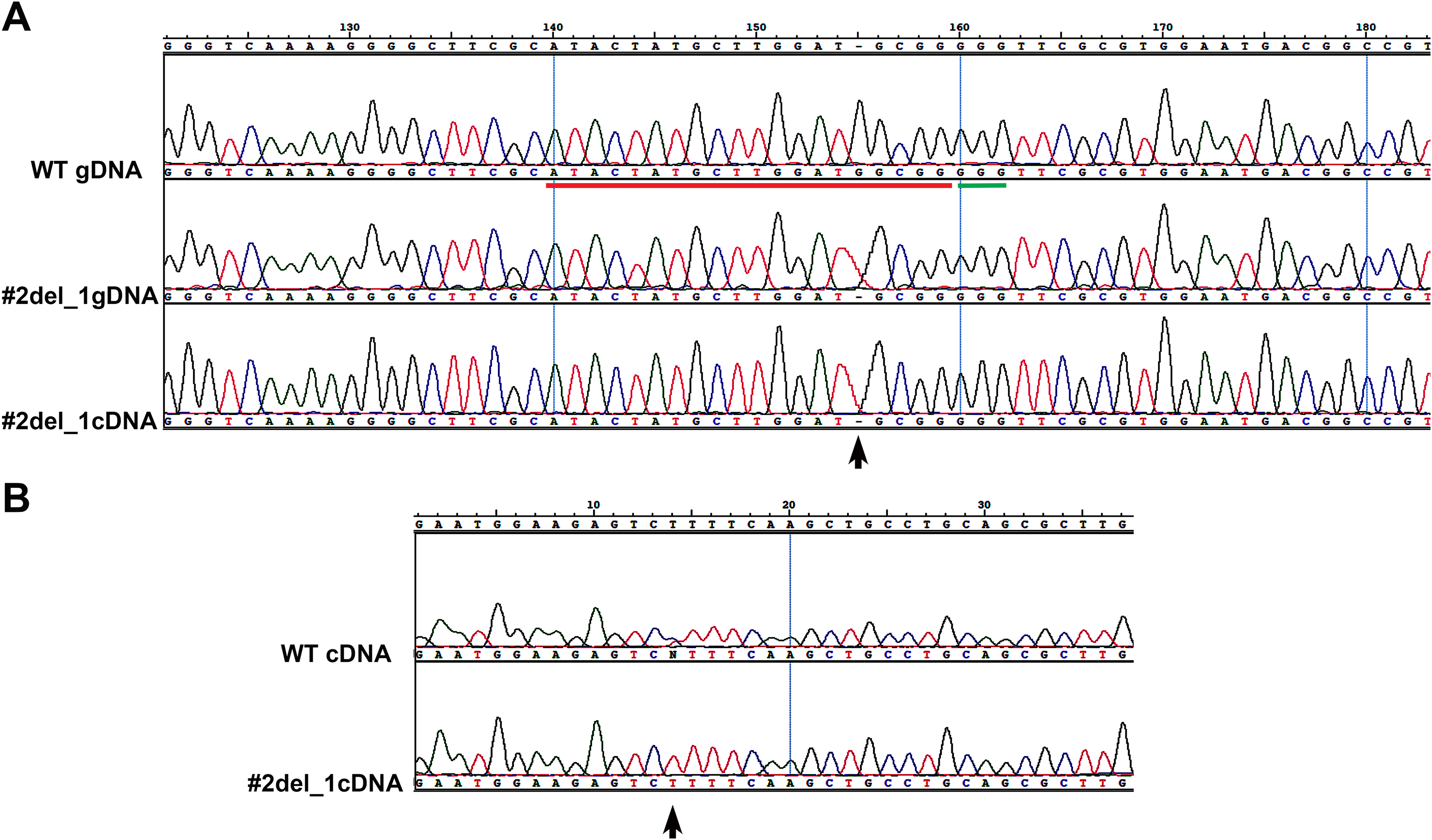



Assessment Of Genomic Changes In A Crispr Cas9 Phaeodactylum Tricornutum Mutant Through Whole Genome Resequencing Peerj




Figure 3 From Crispr Interference Crispri For Sequence Specific Control Of Gene Expression Semantic Scholar




Crispr Plant



Dspace Mit Edu Bitstream Handle 1721 1 Nihms Pdf Sequence 2 Isallowed Y




Off Target Effects In Crispr Cas9 Mediated Genome Engineering Abstract Europe Pmc



Sgrnacas9 A Software Package For Designing Crispr Sgrna And Evaluating Potential Off Target Cleavage Sites



1
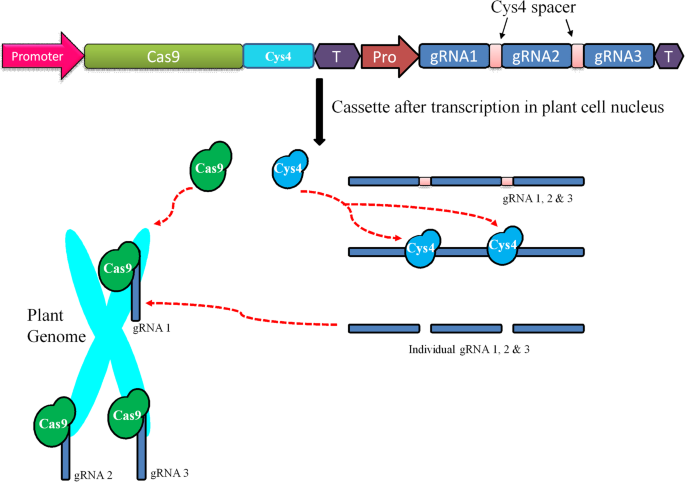



The Present And Potential Future Methods For Delivering Crispr Cas9 Components In Plants Journal Of Genetic Engineering And Biotechnology Full Text




Protein Engineering Strategies To Expand Crispr Cas9 Applications



Team Cu Boulder Project Modeling 14 Igem Org




The Complete Guide To Understanding Crispr Sgrna
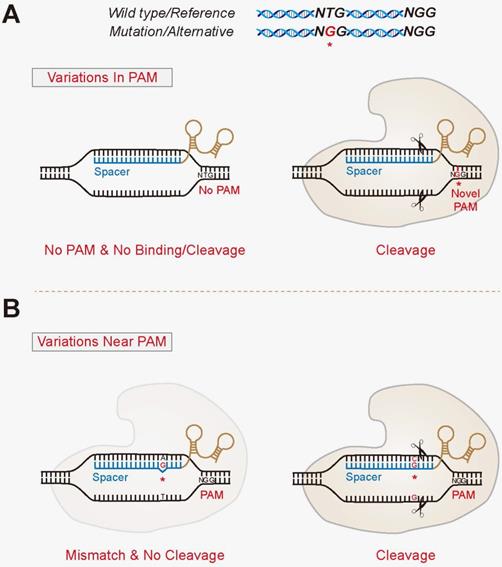



Allele Specific Genome Targeting In The Development Of Precision Medicine




Target Dependent Nickase Activities Of The Crispr Cas Nucleases Cpf1 And Cas9 Abstract Europe Pmc



Crispr Rt



Team Scu China Project Regulation 18 Igem Org



Academic Oup Com Pcp Article Pdf 59 8 1608 Pcy079 Pdf
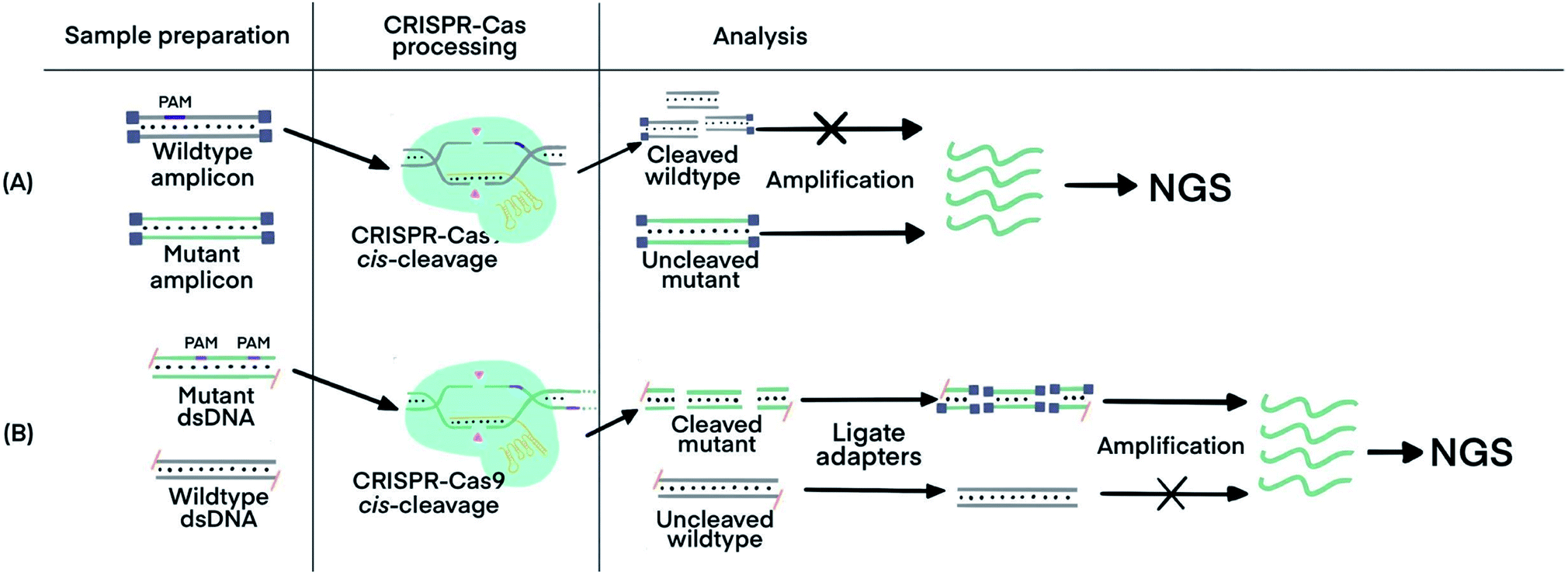



Crispr Technology Incorporating Amplification Strategies Molecular Assays For Nucleic Acids Proteins And Small Molecules Chemical Science Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D0scf



1



Crispr Rt




Target Specificity Of The Crispr Cas9 System




In Our Image The Ethics Of Crispr Genome Editing




A Model For Cas9 Target Binding And Cleavage A In The Unbound State Download Scientific Diagram
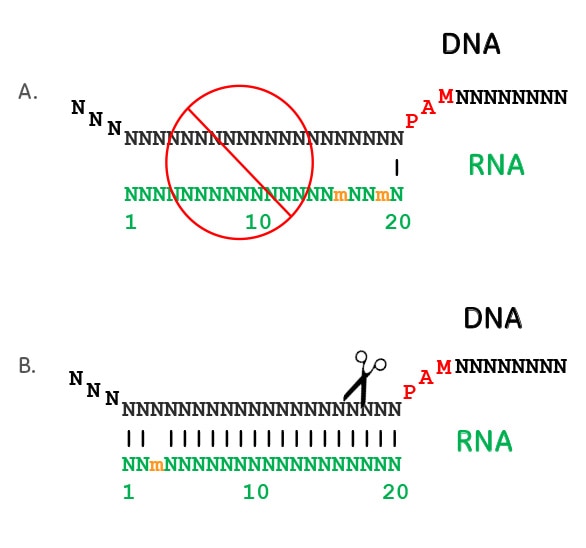



Crispr Cas9 Guide Rna Specificity



A Cas9 Is Directed To A Specific Genomic Target By The First Nt Of Download Scientific Diagram
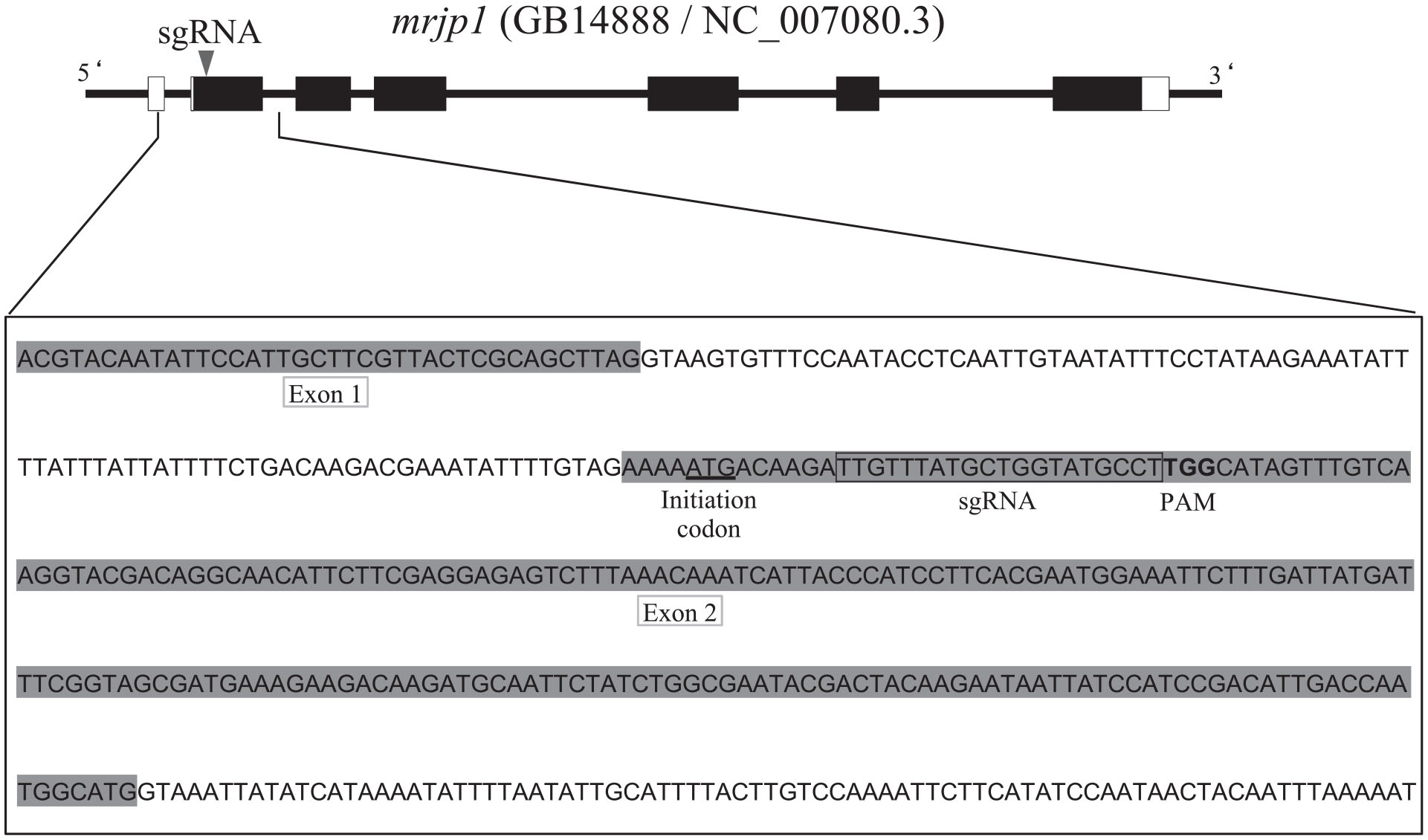



Production Of Knockout Mutants By Crispr Cas9 In The European Honeybee Apis Mellifera L




Research Progress Of Gene Editing Technology Crispr Cas9 System In Animal Gene Editing




5 Key Steps To Successful Crispri Technology Networks




Addgene Crispr Guide




Crispr Cas9 Abm Inc




Scope Flexible Targeting And Stringent Carf Activation Enables Type Iii Crispr Cas Diagnostics Biorxiv
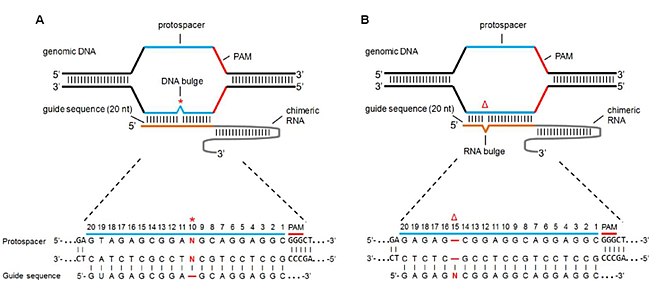



Off Target Genome Editing Wikipedia
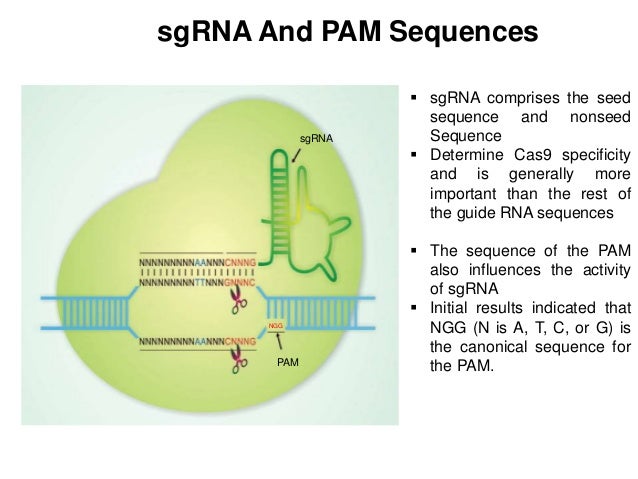



Wnzi Hvusfgimm




Schematic Illustration Of The Crispr Cas9 System Structure And The Download Scientific Diagram
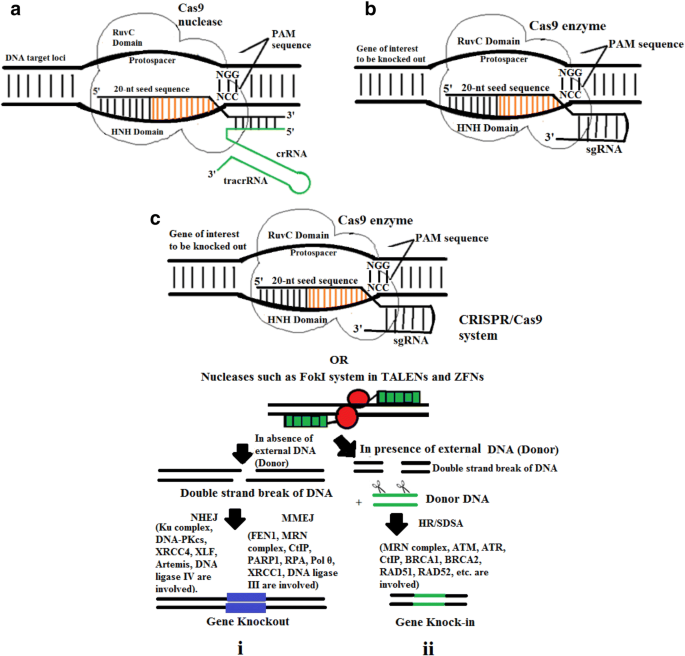



Genome Editing Of Potato Using Crispr Technologies Current Development And Future Prospective Springerlink




Off Target Genome Editing Wikipedia
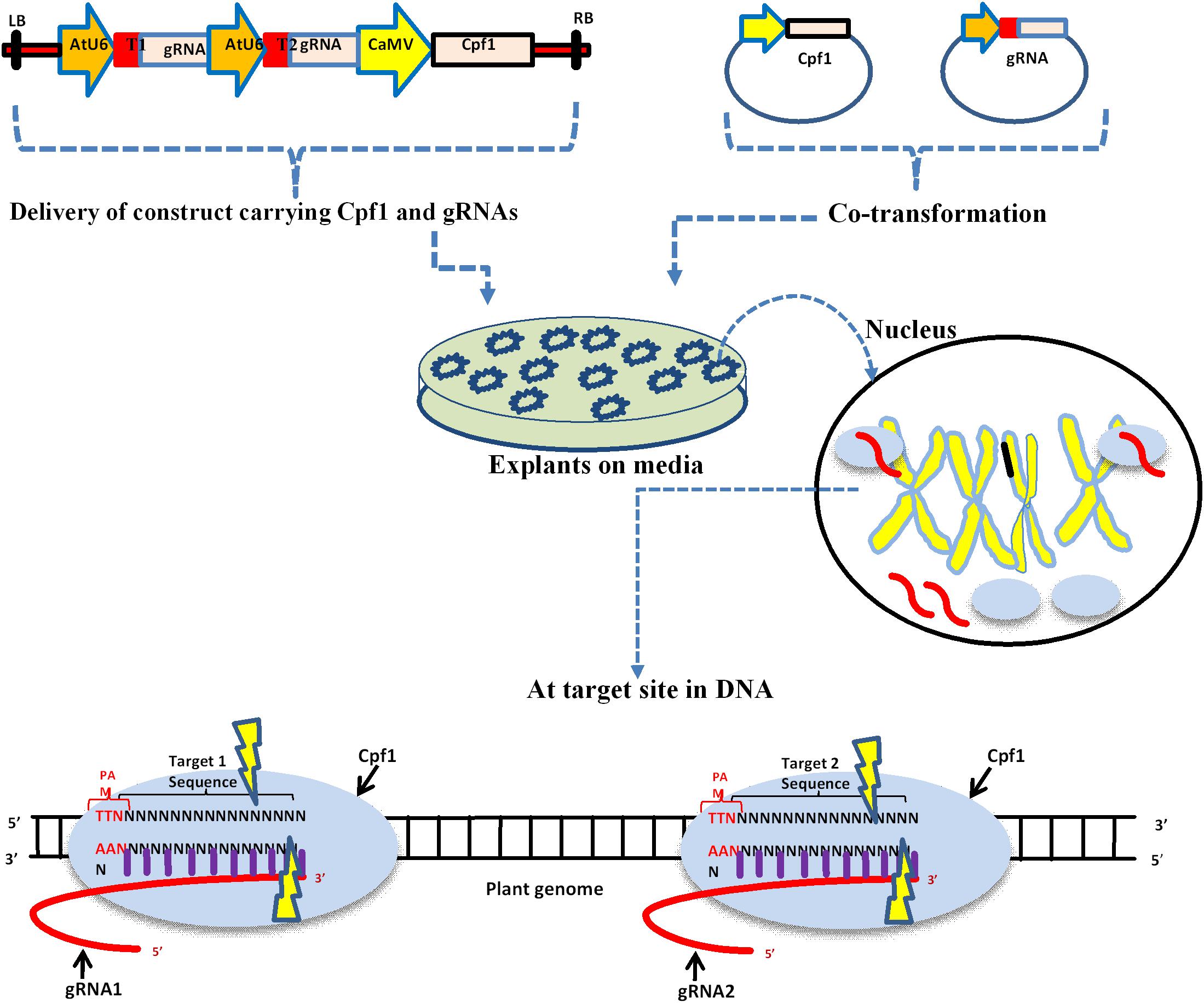



Frontiers The Rise Of The Crispr Cpf1 System For Efficient Genome Editing In Plants Plant Science




Dual Sgrna Based Targeted Deletion Of Large Genomic Regions




Target Sequence Requirements Of A Type Iii B Crispr Cas Immune System Journal Of Biological Chemistry



Www Diva Portal Org Smash Get Diva2 Fulltext01 Pdf
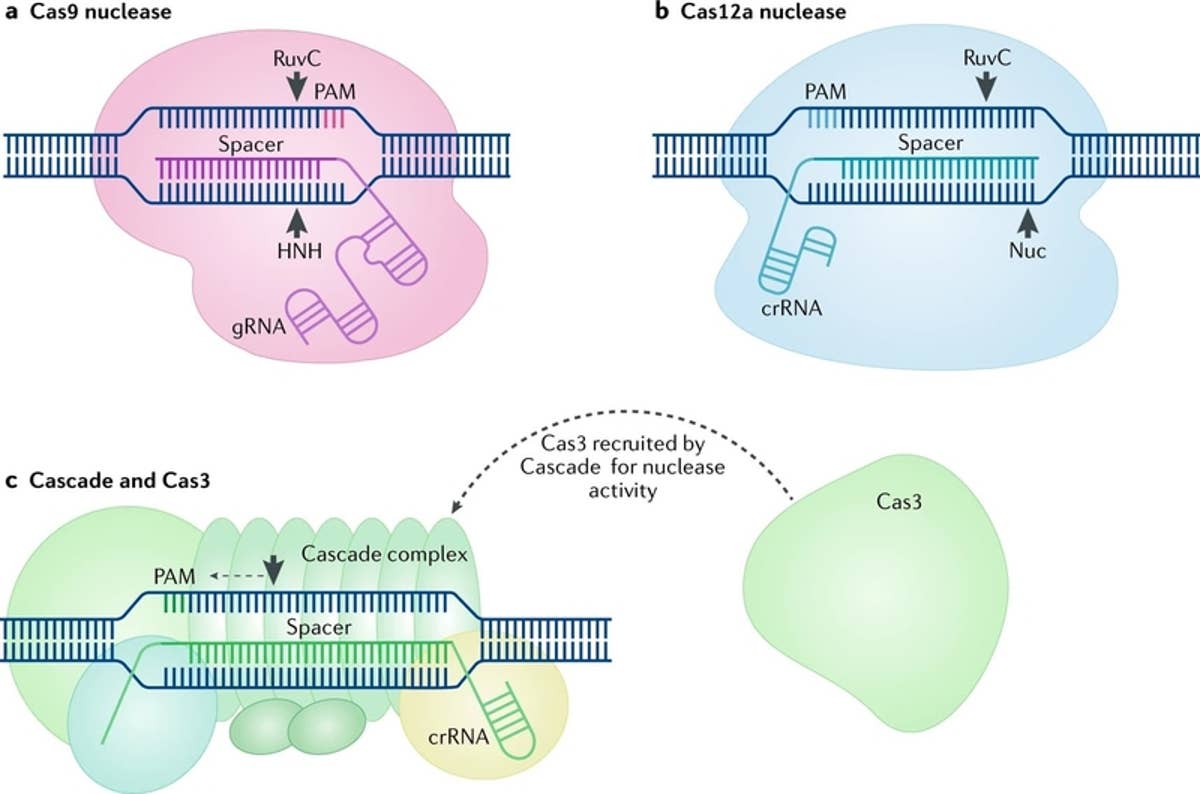



How To Choose The Right Cas9 Variant For Every Crispr Experiment


